Goldshore pulls up high-grade intercepts from QES Zone at Moss Lake – Richard Mills
2022.11.29
In a world of resource depletion, it falls to gold exploration companies to fill the gap with new deposits that can deliver the kind of production required to meet gold demand, which is currently out-running supply. In 2021, 4,021 tonnes of gold demand minus 3,560.7t of gold mine production left a deficit of 460.3t. Only by recycling 1,150t of gold jewelry could the demand be met.
One of my favorite gold juniors is Goldshore Resources (TSXV:GSHR, OTC:GSHRF, FRA:8X00), which just released an open-pit-constrained resource estimate on its flagship Moss Lake Project, with ample room for expansion.
Goldshore reaches significant milestone
For the past year and a half, Goldshore has been advancing the project located near Thunder Bay, Ontario, through detailed field work including a massive 100,000-meter drill program.
Drilling so far has demonstrated that the property contains a significant volume of +1 grams per tonne (g/t) Au mineralization that underpins a meaningful gold deposit.
Before we get into the latest drill results, at the QES Zone, we place the news in the context of the gold market, which continues to experience tightness due to difficulties expanding existing deposits, and a pronounced lack of large discoveries in recent years.
Peak gold
The concept of peak gold should be familiar to most readers, and gold investors. Like peak oil, it refers to the point when gold production is no longer growing, as it has been, by 1.8% a year, for over 100 years. It reaches a peak, then declines.
Peak gold doesn’t necessarily mean gold production will suffer a major fall. However it does mean the mining industry lacks the capacity to ramp up production to meet rising demand; even higher prices would not make that happen, because there aren’t enough mines to tap for more supply.
If gold is indeed becoming scarcer, prices have only one way to go and that’s up, so long as demand for the precious metal is constant or growing.
In a previous article we proved peak mined gold in 2020.
The latest full-year World Gold Council report shows a 1% decline in total gold supply in 2021, compared to 2020, with a sharp drop in recycling more than offsetting higher mine production, which rose 2%, clawing back some of the pandemic-driven losses seen in 2020.
Recycled gold (jewelry) supply fell 11% year on year, a reaction to the modestly lower gold price in 2021 compared to 2020, when gold soared on account of pandemic-related fears, and record-low sovereign bond yields resulting in negative real interest rates — always bullish for gold.
According to WGC, mine production in Q4 2021 fell 1% yoy to 915t. This represented the lowest level of Q4 mine output since 2015. Annual production totalled 3,561t in 2021, 2% higher than 2020 but still lower than 2019 and 3% lower than 2018 — the year when the most gold ever was mined.

In 2019 gold demand reached 4,355.7 tonnes.
The World Gold Council (WGC) reports that 2019 mine production was 3,463.7t.
Gold jewelry recycling was 1,304t, bringing total gold supply in 2019 to 4,776.1t.
If we stop there, we show a slight gold supply surplus of 420 tonnes. Peak gold debunked!
Not so fast, let’s think about those numbers for a minute. In calculating the true picture of gold demand versus supply, we, at AOTH don’t, and won’t, count jewelry recycling. What we want to know, and all we really care about, is whether the annual mined supply of gold meets annual demand for gold. It doesn’t! When we strip jewelry recycling from the equation, we get an entirely different result. i.e. 4,355 tonnes of demand minus 3,463 tonnes of production left a deficit of 892 tonnes.
Let’s fast forward two years, in 2021 total gold supply including jewelry recycling reached 4,666.1 tonnes. Full-year demand was 4,021 tonnes, propelled by Q4 2021 demand which jumped almost 50% to a 10-year high.


No peak gold here, right? Demand is more than satisfied by supply.
But when we strip jewelry recycling from the equation, 1,149.9t, we get 4,021 tonnes of demand minus 3,560.7t of mine production leaves a deficit of 460.3t.
This is significant, because it’s saying even though major gold miners are high-grading their reserves, mining all the best gold and leaving the rest, they still didn’t manage to satisfy global demand for the precious metal, not even close. Only by recycling thousands of tonnes of gold jewelry over the last few years could demand be satisfied.
This is our definition of peak gold. Will the gold mining industry be able to produce, or discover, enough gold, so that it’s able to meet demand without having to recycle jewelry? If the numbers reflect that, peak gold would be debunked. We’ve been tracking it since 2019, and it hasn’t happened yet.
As gold mining companies struggle to keep up with demand, we at AOTH see nothing but blue sky ahead for the precious metal.
Let’s turn to hard evidence, such as AOTH’s own research, and a report by Wood Mackenzie on just how valuable the world’s potential future gold mines, mostly controlled by junior resource companies, will be to miners looking to replace reserves.
Woodmac says to avoid a perpetual decline in mined gold, the industry must see a rise in the number of gold projects under development that have a good chance of becoming mines.
How many projects? 44, to be exact. The research firm crunched the numbers in 2020, and found that by 2025 the industry will need to commission 8Moz of projects.
Intuitively, that seems virtually impossible – Wood Mackenzie agrees.

“If all our probable projects were to come online before 2025, this would almost meet the requirement to maintain 2019 production levels,” said Rory Townsend, Wood Mackenzie’s head of gold research.
“The likelihood, however, is that we see some degree of slippage among a number of these assets due to permitting delays, prioritization of other capital projects and changes in scope,” said Townsend.
Consider: in the 1970s, ‘80s and ‘90s, the gold industry found at least one +50Moz gold deposit and ten +30Moz deposits. Since 2000, no deposits of this size have been found, and very few 15Moz deposits.
Don’t believe us? Here’s Ian Telfer, former Goldcorp chairman, and gold industry expert, giving his argument for peak gold, in 2018:
“In my life, gold produced from mines has gone up pretty steadily for 40 years. Well, either this year it starts to go down, or next year it starts to go down, or it’s already going down… We’re right at peak gold here.”
To get world gold mine production back to the point where it can meet the required annual demand without recycling jewelry, the industry has two choices: it can mine more gold, or it can discover new gold.
Squeezing more gold out of existing deposits has its challenges. Reserves are getting depleted, and mines are having production problems, including lower grades, labor disruptions, protests, etc. Remember, to avoid a perpetual declined in mined gold, by 2025 the industry will need to commission 8Moz of projects (Wood Mackenzie).
This week it was reported that Burkina Faso, the 12th largest gold mining country in the world, is set to produce 13% less gold this year than in 2021, due to mine closures. Mines there are closing because of security risks to employees; 2022 is shaping up to be the deadliest year since a civil conflict began a decade ago, pitting the government of Burkina Faso against Islamic militants affiliated with Al Qaeda.
But finding and exploiting new gold deposits is even harder, more expensive and risky.
Few gold exploration projects have the economics, scale, jurisdiction and money-raising capabilities backing them, to become mines. Those with the staying power to make it through the various development stages, from initial discovery to drilling to resource definition to first production, will be the belle of the ball, so to speak, with many major gold miners cueing up for the first dance. Cue Goldshore Resources.
Moss Lake Project
Its Moss Lake Project consists of 282 mining claims for a total area of 14,292 hectares, hosting a number of gold and base metals-rich deposits, all of which occur over a mineralized trend exceeding 20 km.
A new mineral resource estimate was just published by Goldshore on the Moss Lake deposit (see below).
A historical mineral resource estimate was completed on the East Coldstream deposit in 2011 by Foundation Resources. The deposit is a shear-hosted disseminated style, which outcrops at surface. It has been drilled over a 1.3 km length and to depths of 200m, with 138 holes completed between 1988 and 2017. The deposit remains largely open at depth and may have the potential for expansion along strike. Historical drill hole highlights include 4.86 g/t Au over 27.3m.
The past-producing North Coldstream Mine is reported to have produced significant amounts of copper, gold and silver, from mineralization with potential iron-oxide-copper-gold deposit-style affinity. The exploration potential immediately surrounding the mining area is not currently well understood and historical data compilation is required.
The Hamlin Zone is a significant occurrence of copper and gold mineralization, and is also a potential iron oxide copper gold (IOCG) deposit. From 2008-11, Glencore tested Hamlin with 24 drill holes which successfully outlined a broad and intermittently mineralized zone over a strike length of 900m. Historical drill hole highlights from the Hamlin Zone include 0.9 g/t Au and 0.35% Cu over 150.7m.
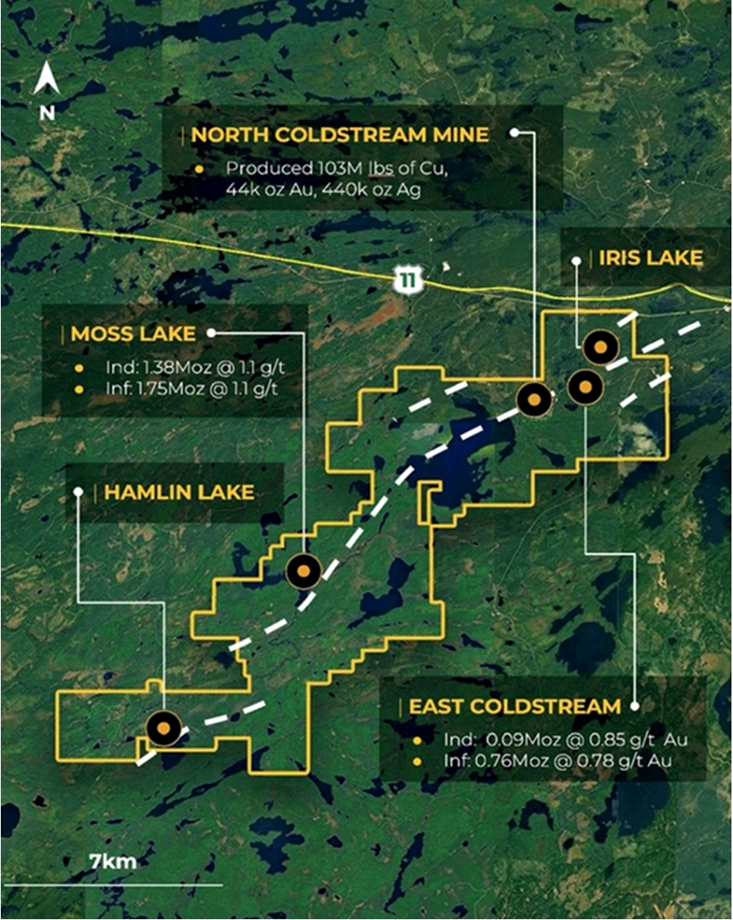
Goldshore Resources’ Moss Lake Project is in an excellent jurisdiction with a number of major gold deposits nearby, including Detour Lake (Kirkland Lake Gold) with 15.7Moz proven and probable at 0.82 g/t Au, New Gold’s Rainy River with 2.6Moz P&P at 1.06 g/t Au, and Cote’s (IAMGOLD & Sumitomo) 7.3Moz P&P at 1.0 g/t Au.

Goldshore’s new mineral resource estimate (MRE) includes the assay results from 48 holes drilled during the 2021-22 drill campaign.
As the table below shows, the MRE is divided into two domains, a shear domain and an intrusion domain.

The higher-grade shear domain consists of 34.7 million tonnes grading 2.0 grams per tonne (g/t) Au (gold) for 2.20 million ounces of contained metal.
The intrusion domain is 87Mt @ 0.7% Au, for 1.97Moz of contained metal. In total the MRE consists of 121.7Mt @ 1.1 g/t Au, for total contained metal of 4.17Moz.
These numbers are based on a $1,500 gold price and a cut-off grade of 0.4 g/t Au.
According to Goldshore, the shear domain represents an opportunity for a high-grade open-pit gold resource. There is also “significant and clear expansion potential” through strike and dip extensions to known shears, as well as parallel shears.
The MRE greatly enlarges the historical (2013) resource estimate, with 35% more tonnage and 33% more contained gold ounces.
The company says the project hosts 29 additional targets over a 35-km trend, which it continues to evaluate.
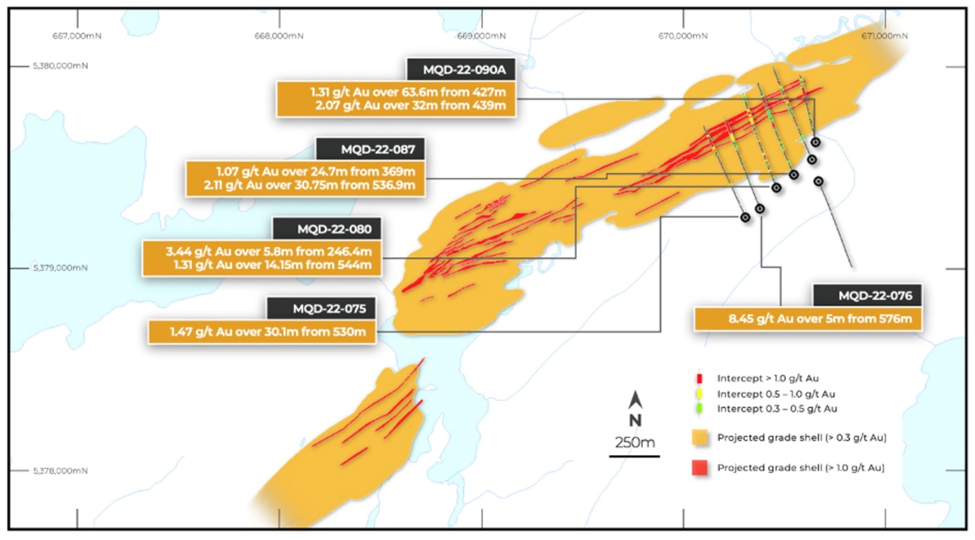
This week, Goldshore released assay results from seven holes drilled into the QES Zone, from its ongoing 100,000-meter drill program. The holes are among the 52 that missed the Oct. 14 deadline for the recent MRE. However, according to President & CEO Brett Richards, “They confirm our belief that there are additional high-grade shear zones within the deposit that will potentially add to the shear domain component of the mineral resource that we anticipate will be prioritized in the mining schedule when we move towards conducting a preliminary economic analysis next year.”
Richards made the comments in a Nov. 28 news release detailing the company’s latest assay results from the Moss Lake Project.
Drilled to expand the coverage of the high-grade shears in the QES Zone, the results confirmed higher-grade shear-hosted gold mineralization within a large volume of well-mineralized diorites (a diorite is a type of igneous intrusive rock). According to Goldshore, These results are all within the $1,500 Whittle pit that constrains the current resource and identifies new high-grade shears. Best intercepts include:
- 1.47 g/t Au over 30.1m from 530.0m in MQD-22-075;
- 8.45 g/t Au over 5.0m from 576m depth in MQD-22-076 including
- 36.9 g/t Au over 1.0m from 577m;
- 1.07 g/t Au over 24.7m from 369.0m depth in MQD-22-087 and
- 2.11 g/t Au over 30.75m from 536.9m including
- 11.5 g/t Au over 3.1m from 555.2m;
- 1.31 g/t Au over 63.6m from 427.0m depth in MQD-22-090A including
- 2.07 g/t Au over 32.0m from 439.0m.

Assays have been received for six holes that have infilled areas of the QES Zone that are between sections drilled by historical holes with collar survey problems. As a result, they will replace the low-confidence historical holes in the upcoming resource model update.
As with the historical holes, these holes intersected several broad zones of low-grade mineralization within the altered diorite intrusion host. Examples include:
- 0.77 g/t Au over 83m from 493m depth in MQD-22-075;
- 0.71 g/t Au over 131.1m from 493m in MQD-22-076;
- 0.54 g/t Au over 102m from 476m and 0.78 g/t Au over 70m from 419m in MQD-22-085;
- 0.50 g/t Au over 115.9m from 408.1m in MQD-22-087.
All these low-grade zones occur as envelopes to higher-grade structures that form a three-dimensional shear network that has developed in response to strain on the altered diorite intrusion, the company states.
An additional parallel shear was discovered within the intermediate volcanic package about 150m south of the main QES system, which contains broad intercepts of low-grade mineralization including 0.91 g/t over 24.8m from 246.4m in MQD-22-080; 0.42 g/t over 39.0m from 189.0m in MQD-22-087 containing higher-grade intercepts including 3.44 g/t Au over 5.8m from 246.4m depth in MQD-22-080.
Importantly, these intercepts identified additional high-grade shears not modeled in the recent MRE. Pete Flindell, Goldshore’s VP Exploration, said he expects them to be included in the next mineral resource update early next year.
Next steps
Along with re-logging/ re-sampling historical drill core, and downhole surveying where possible, Goldshore plans to accurately define the shear-hosted and intrusive domain mineralization, through selective re-drilling of historical holes.
Work has also commenced on a metallurgical testing program led by Ausenco, an Australia-based engineering firm. Once complete, Goldshore expects to start a (new) preliminary economic assessment (PEA), slated for completion in 2023.
Infill drilling, re-sampling of historical drill holes, and geological modeling will continue throughout the coming months to support a resource estimate update that upgrades the inferred resources to indicated. This work is targeted for completion by the end of 2023, when the company expects to start a prefeasibility study.
Goldshore Resources Inc.
TSXV:GSHR, OTC:GSHRF, FRA:8X00
Cdn$0.24, 2022.11.28
Shares Outstanding 143.8m
Market cap Cdn$34.9m
GSHR website
Richard (Rick) Mills
aheadoftheherd.com
subscribe to my free newsletter
Legal Notice / Disclaimer
Ahead of the Herd newsletter, aheadoftheherd.com, hereafter known as AOTH.
Please read the entire Disclaimer carefully before you use this website or read the newsletter. If you do not agree to all the AOTH/Richard Mills Disclaimer, do not access/read this website/newsletter/article, or any of its pages. By reading/using this AOTH/Richard Mills website/newsletter/article, and whether you actually read this Disclaimer, you are deemed to have accepted it.
Any AOTH/Richard Mills document is not, and should not be, construed as an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to purchase or subscribe for any investment.
AOTH/Richard Mills has based this document on information obtained from sources he believes to be reliable, but which has not been independently verified.
AOTH/Richard Mills makes no guarantee, representation or warranty and accepts no responsibility or liability as to its accuracy or completeness.
Expressions of opinion are those of AOTH/Richard Mills only and are subject to change without notice.
AOTH/Richard Mills assumes no warranty, liability or guarantee for the current relevance, correctness or completeness of any information provided within this Report and will not be held liable for the consequence of reliance upon any opinion or statement contained herein or any omission.
Furthermore, AOTH/Richard Mills assumes no liability for any direct or indirect loss or damage for lost profit, which you may incur as a result of the use and existence of the information provided within this AOTH/Richard Mills Report.
You agree that by reading AOTH/Richard Mills articles, you are acting at your OWN RISK. In no event should AOTH/Richard Mills liable for any direct or indirect trading losses caused by any information contained in AOTH/Richard Mills articles. Information in AOTH/Richard Mills articles is not an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any security. AOTH/Richard Mills is not suggesting the transacting of any financial instruments.
Our publications are not a recommendation to buy or sell a security – no information posted on this site is to be considered investment advice or a recommendation to do anything involving finance or money aside from performing your own due diligence and consulting with your personal registered broker/financial advisor.
AOTH/Richard Mills recommends that before investing in any securities, you consult with a professional financial planner or advisor, and that you should conduct a complete and independent investigation before investing in any security after prudent consideration of all pertinent risks. Ahead of the Herd is not a registered broker, dealer, analyst, or advisor. We hold no investment licenses and may not sell, offer to sell, or offer to buy any security.
Richard does not own shares of Goldshore Resources Inc. (TSXV:GSHR). GSHR is a paid advertiser on his site aheadoftheherd.com
Legal Notice / Disclaimer
Ahead of the Herd newsletter, aheadoftheherd.com, hereafter known as AOTH.Please read the entire Disclaimer carefully before you use this website or read the newsletter. If you do not agree to all the AOTH/Richard Mills Disclaimer, do not access/read this website/newsletter/article, or any of its pages. By reading/using this AOTH/Richard Mills website/newsletter/article, and whether you actually read this Disclaimer, you are deemed to have accepted it.