Atmospheric Rivers Have Shifted Towards Earth’s Poles, Bringing Big Changes To Weather
By Tom Hale – IFL Science
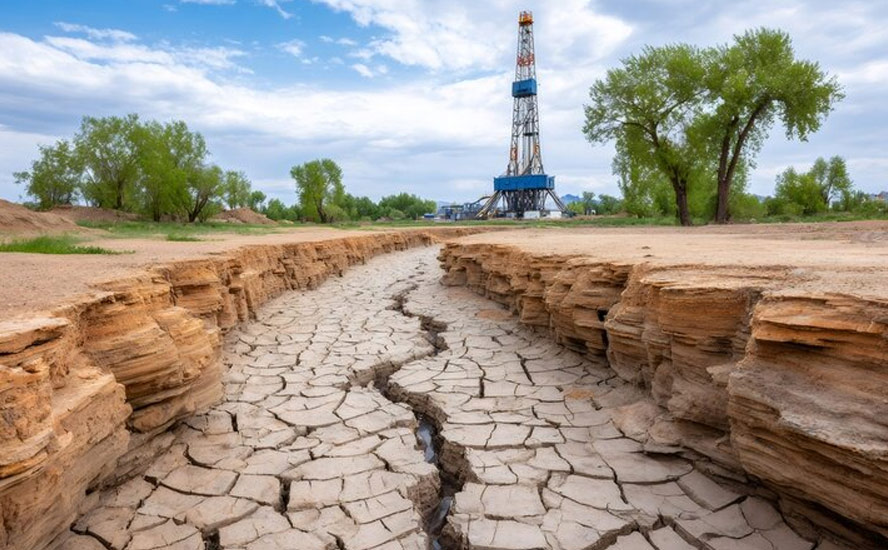
In recent decades, atmospheric rivers that transport water vapor high above the Earth’s surface have shifted position – a radical change that could have an impact on weather patterns and rainfall across the planet.
Scientists at UC Santa Barbara found that atmospheric rivers in both hemispheres have moved approximately 6° to 10° closer to the poles over the past 40 years. This means that the areas affected by atmospheric rivers are farther north in the Northern Hemisphere and farther south in the Southern Hemisphere than they used to be.
Legal Notice / Disclaimer
Ahead of the Herd newsletter, aheadoftheherd.com, hereafter known as AOTH.Please read the entire Disclaimer carefully before you use this website or read the newsletter. If you do not agree to all the AOTH/Richard Mills Disclaimer, do not access/read this website/newsletter/article, or any of its pages. By reading/using this AOTH/Richard Mills website/newsletter/article, and whether you actually read this Disclaimer, you are deemed to have accepted it.
Share Your Insights and Join the Conversation!
When participating in the comments section, please be considerate and respectful to others. Share your insights and opinions thoughtfully, avoiding personal attacks or offensive language. Strive to provide accurate and reliable information by double-checking facts before posting. Constructive discussions help everyone learn and make better decisions. Thank you for contributing positively to our community!
1 Comment
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
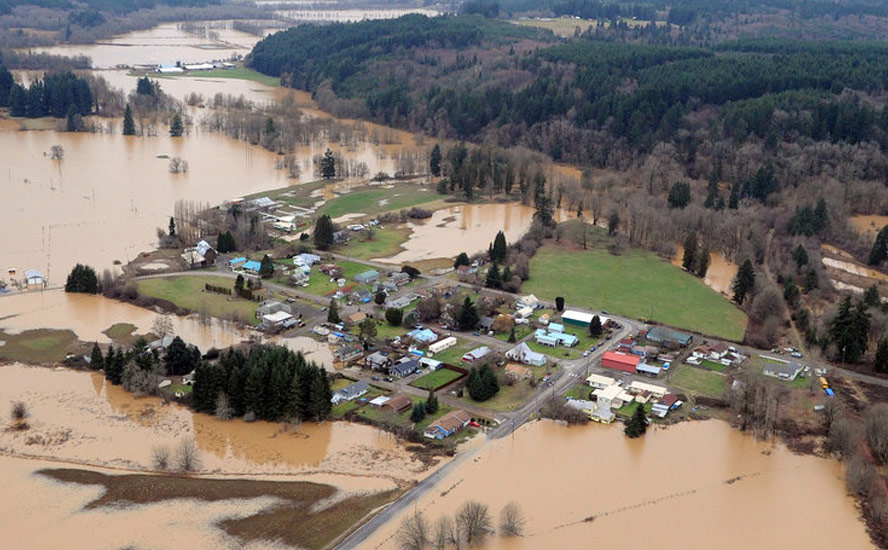



























#atmosphericrivers