Microplastics found in farm animals for the first time; Evanesce Packaging Solutions offers alternative to single-use plastics
2022.07.13
The next time you barbecue a piece of meat, you may also be grilling plastic and unwittingly ingesting it.
The shocking revelation comes via The Guardian, which ran an article this week declaring that microplastic contamination has been reported in beef and pork for the first time, as well as in the blood of cows and pigs reared on farms.
In a pilot study, Dutch scientists found tiny plastic particles in 75% of meat and milk products tested and in every blood sample. The same group of researchers from the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VUA) in March found microplastics in human blood for the first time. That discovery was alarming because it means that plastic particles can travel around the body and may lodge in organs.
The farm animal study suggests that plastic is finding its way into them via the feed they ingest. Particles were identified in every sample of animal pellet feed tested; the food products were packaged in plastic.
According to The Guardian,
The scientists tested 12 samples of cows’ blood and 12 of pigs’ blood and found microplastics in all of them, including polyethylene and polystyrene. The 25 milk samples included milk from supermarket cartons, milk tanks on farms and hand-milking. Eighteen of the samples, including at least one of each type, contained microplastics.
Seven of the eight beef samples and five of the eight pork samples were contaminated.
Our plastic world
Plastic has been filling up our landfills for decades, or incinerated, thus contributing to land/ ocean/ air pollution, and carbon emissions.
If plastic were a country, it would be the fifth-highest emitter in the world. That’s because 99% of plastic is made from fossil fuels. A significant portion of emissions comes from the extraction and transportation of fuels that create plastic, including methane from natural gas, considered 28 times more potent than carbon dioxide. Cracking plants that refine fuel and convert it to plastic are also extremely harmful to the environment. At the production stage, polyester, polyamide and acrylic, used in textiles, have the highest level of emissions.
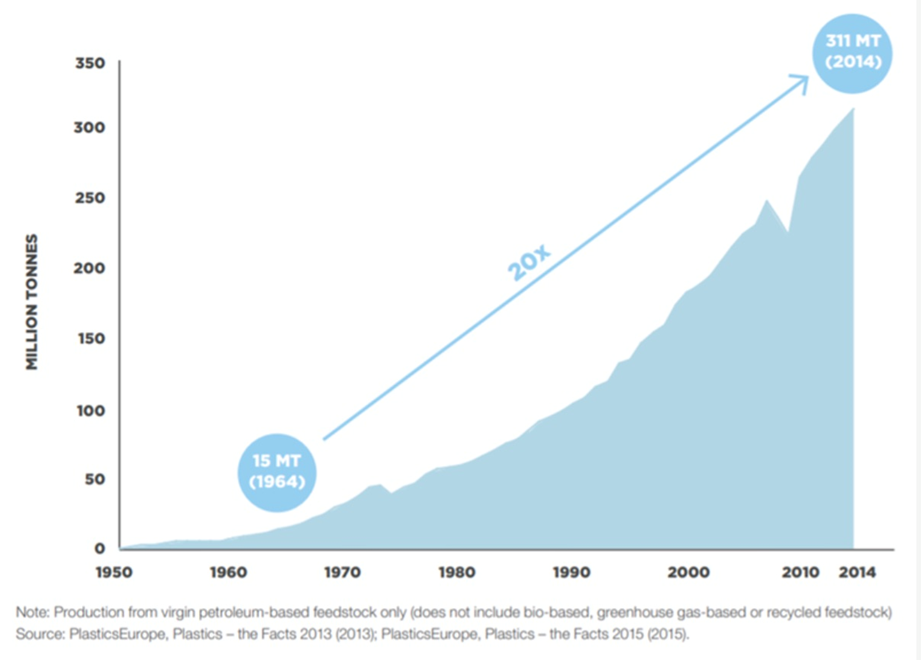
Over the years, plastic has followed a hockey stick-shaped growth trajectory. We make 190 times more plastic than we did in 1950.
A 2016 study by the World Economic Forum estimates that global plastic production went from 15 million tonnes in 1964 to 311 million tonnes in 2014 — a 20-fold increase during a 50-year period. Now, the world produces more than 380 million tonnes of plastic, up to 50% of which are for single use.
Production is expected to at least double again over the next two decades, then quadruple by 2050, the WEF predicts.
Despite the proliferation of curbside recycling programs, regional eco-centers, and an increasingly aware and motivated public, very little plastic is recycled, around 10% according to most estimates. Another 12% is incinerated, reducing it to ash, gas and heat. The other 79% makes its way to a landfill or escapes into the environment.
It is estimated there are over 150 million tonnes of plastic in the ocean. Around 8 million tonnes enter the seas every year — the equivalent of dumping a truckload of plastic garbage every minute.
National Geographic says the problem of discarded plastic is so severe, that if nothing is done, by 2050 the oceans will contain more plastic than fish, ton for ton.
It has become a much-discussed topic, and the subject of several docuseries, revolving around the harmful effects of minute plastic fragments, called microplastics and nanoplastics, on plants, fish, sea birds, mammals, and eventually, humans at the top of the food chain.
The problem stems from the fact that plastic is virtually indestructible. A trait that was once sold to consumers as a virtue, has become a vice, due to the ubiquity of plastic especially in the marine environment.
Most plastic has a very long lifespan. Plastic bags, for example, can take up to 20 years to decompose, while takeaway coffee cups, despite being mostly paper, have a plastic lining that will endure for 30 years.
Other items, including coffee pods, disposable diapers, and plastic toothbrushes, will be in landfills for five centuries!

What makes plastic so problematic? The answer comes down to chemistry. Plastic is a polymer molecule consisting of repeating identical units (homopolymer) or different sub-units in sequences (copolymer). Plastics are further categorized as thermoplastics, which soften when heated and can be molded; or thermosets, which cannot be molded or heated.
Both types cause pollution in a marine environment.
Plastics also contain chemicals to improve their properties, that cause harm when they enter the food chain.
Although hundreds of thousands of plastic materials have been invented, only six are extensively used: polyethylene terephthalate (PETE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC-U), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS), or Styrofoam.
One of the surprising facts about microplastics is how entrenched they are in the global ecosystem. They have been detected in lakes and seas, in the sediments of rivers and deltas, and in the stomachs of the smallest and largest organisms, from zooplankton to whales. One study found that every square kilometer of the world’s oceans has 63,320 plastic particles floating on the surface.

Effects on human health
Every week, people consume an amount of plastic the size of a credit card.
Especially worrying are “nanoplastics” — pieces that are so tiny, they are able to penetrate human cell walls.
Potential adverse effects, at high enough concentrations, may include immunotoxicological responses, reproductive disruption, anomalous embryonic development, endocrine disruption, and altered gene expression. High volumes of microplastics in rats have been found to cause cancer.
While microplastics’ effects on human health have not been widely studied, it’s safe to say that inhaling or ingesting them should be avoided. This may be extremely difficult however; one study found plastic fibers in 87% of the human lungs studied.
Recently, microplastics were found in human placentas, though more research is needed to determine if this is a widespread problem. Another found that microplastics can latch onto the outer membranes of red blood cells and may limit their ability to transport oxygen.
A haunting discovery was made earlier this year, when scientists from Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam detected polymer particles in human blood for the first time, raising alarm bells for our future survival in a world full of plastics.
“Our study is the first indication that we have polymer particles in our blood – it’s a breakthrough result,” Professor Dick Vethaak, an ecotoxicologist at the university, told The Guardian.
Vethaak’s previous work had shown that microplastics were 10 times higher in the feces of babies compared with adults, and that babies fed with plastic bottles are swallowing millions of microplastic particles a day.
Chemicals associated with plastics are known to be harmful. The most well-studied is BPA — found in plastic packaging or food storage containers. When BPA leaks into food it can interfere with reproductive hormones in women.
Another chemical, phthalates, is used to make plastic flexible. The presence of phthalates in a petri dish was shown to increase the growth of breast cancer cells.
In a limited study, Canadian researchers estimated the average person ingests over 74,000 plastic particles a year. Examining just a few food categories including fish, shellfish, sugar, alcohol, honey, bottled versus tap water, plus air, the study authors found the most microplastics in air, bottled water and seafood.
Vectors
There are a number of ways that plastics get into the environment. Microbeads used as exfoliants in beauty products escape water filtration systems. Other primary sources include plastic powders in molding, and plastic nanoparticles in a variety of industrial processes.
The extensive and indiscriminate use of food packaging, car tires, paints, personal care products (e.g. toothpaste) and electronic equipment, are some more contributors to microplastic contamination.
Microplastics can also become part of the water cycle and delivered back to Earth as rain or snow.
Scientists think that tiny particles shed by anything plastic get incorporated into water droplets when it rains, then wash into lakes, rivers and oceans. When the water evaporates, the particles can end up in groundwater. They are then consumed by animals and people via drinking water and food, or breathed in.
If nano-scale plastic has become prevalent in drinking water, oceans, rainwater, and the animals that mistakenly eat them (or can’t avoid them because they’re in their feed), it’s not a stretch to find microplastics in our food.
According to Food Safety magazine, microplastics are present in various food products, including seafood and bottled water. Microplastics can also help introduce other contaminants to foods. Persistent organic pollutants and other toxins in water can also be attracted to these particles. Once consumed by plankton, these contaminants are passed through the food chain to small fish and eventually to humans.
As mentioned, microplastics were recently found in beef and pork for the first time, as well as in the blood of cows and pigs. The tiny plastic particles are thought to originate in the feed that the animals consume.
One study looking for synthetic particles in sea turtles found microplastics in the guts of all 102 turtles that were examined. They have also been detected in quantities up to 273 particles per pound of sea salt, 300 fibers per pound of honey, and around 109 fragments per liter of beer.
A common way for nanoplastics to move up the food chain, is to be first consumed by algae, that is eaten by water fleas, which in turn become fish food.
The problem is not only the nano/microplastics, but the pollutants they carry with them. When plastics move through the food chain, the attached toxins also move, and accumulate in animal fat and tissue through a process called bio-accumulation. Chemicals added to the plastic during the production process can leach from the plastic into the body of the animal that has eaten them. Read more here

Single-use plastic bans
Thankfully, the news on plastic pollution isn’t all bad; in recent years some positive developments have taken place.
Eighty countries have successfully brought full or partial bans on single-use plastic, including 30 African nations and the European Union. The latest is India.
Several US jurisdictions have enacted policies on plastic pollution. In 2018 Seattle became the first US city to slap a ban on plastic straws and single-use plastic utensils. Eight states — California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Maine, New York, Oregon, and Vermont — have banned single-use plastic bags.
Montreal banned plastic bags thinner than 50 microns in 2018, followed by bans on plastic bags and straws in the Vancouver Island communities of Victoria, Tofino and Uclulet in 2019. On the other side of the country, PEI’s Plastic Bag Reduction Act came into effect on July 1, 2019.
The Canadian government’s promised ban on single-use plastics — items such as shopping bags, cutlery, straws, and food take-out containers — was finally announced this past June. It will come into effect in December. CNBC quotes government data stating that single-use plastics make up most of the plastic waste found on Canadian shorelines, with up to 15 billion plastic shopping bags used each year and about 16 million straws used every day.
In step with increasingly stringent government regulations on single-use plastic, the manufacturing sector has been busy developing technologies that can serve as alternatives to plastic, while maintaining many of its same characteristics.
An example of a company working in this area, one that has recently come to my attention, is Evanesce Packaging Solutions.
Evanesce Packaging Solutions Inc.
Headquartered in Vancouver, Evanesce designs and manufactures sustainable packaging solutions using the latest advancements in material science. The still-private company’s plant-based compostable packaging alternatives, which decompose in 90 days or less, are set to disrupt the industry. Its goal is to eliminate single-use plastic and Styrofoam waste in food packaging, which takes 500 years or more to decompose.
The rapidly expanding sustainable packaging market is expected to reach over US$1.2 trillion by 2028. As a solution to replace single-use plastics and Styrofoam in food services and packaging, Evanesce’s business model includes manufacturing, licensing, collaborative partnerships and joint ventures to accelerate the adoption of compostable plant-based solutions.
Targeting the $980 billion per year single-use plastics (SUP) market, Evanesce is positioning itself to be at the leading edge of the change that is bringing forth alternatives to SUPs.
The company has set up a joint venture partnership with Minima, the world’s leading provider of polylactic acid (PLA) used to make biodegradable plastic. The Taiwanese company is led by CEO and founder Dr. Chien-Ming Huang, whose engineering prowess over the years has made him a leader in the industry, attracting some of the largest chemical and distribution company players to Minima, including China-based Formosa Plastics and Japan’s Mitsui & Co., one of the largest logistics and trading companies in the world.
Through the North American JV, Evanesce is providing a PLA technology that is 81% owned by Evanesce, and 19% by Minima. The joint venture has set up its first operating plant in South Carolina to manufacture straws made from corn starch, that are 100% compostable within 90 days, and will become the initial cornerstone of Evanesce’s business development.
Evanesce’s 100% plant-based, 100% compostable Molded Starch technology can be molded into a diverse range of products including meat trays, cups, food containers and five-section meal trays. Best of all, they cost half of other eco-friendly alternatives.
Its biopolymers are cheaper than paper, better than plastic and BPI-certified compostable. Its range of food service products are made with high-quality 100% plant-based resins and include straws, cups, lids, bowls, plates, cutlery and more.
Last October, Evanesce opened its first US production facility in Hampton County, South Carolina, where it will produce eco-friendly food service products using renewable resources such as corn starch. The 15,000-square-foot facility has the ability to manufacture millions of compostable straws per day. A second plant is planned for northern Las Vegas, Nevada.
A C$10-million financing that closed in November was the second round of funding last year, bringing the total capital raised to over $16 million.
The North American compostable straw market is pegged at around $4 billion a year. Of that, paper straws represent about $1.4 billion. But paper straws have drawbacks that include getting soggy when wet, plus the fact that when it comes right down to it, they aren’t that green. Trees are a natural resource. Cutting them down to make paper straws may be better than letting “forever” plastic straws get into landfills, rivers and oceans, but at the end of the day, it isn’t much better for the environment. Evanesce sees the $1.4B paper straw market as an opportunity ripe for the picking. For one thing, their manufacturing costs are lower.
Evanesce’s compostable straws are also more environmentally friendly, technologically more advanced, and they are better for both the companies that use them (Evanesce’s clients) and their customers.
The company currently has four machines for straw-making and it hopes to scale up to 10 by the end of the year. Within the next two years the goal is to have 14 machines up and running.
Of course, Evanesce isn’t the only company attempting to capitalize on the “greening” of the food and beverage industry, so what distinguishes them from the competition?
The answer comes down to the fact that there are a number of challenges that makers of single-use plastic alternatives face. The first is they typically need several years of engineering under their belt to come up with a product that is compostable yet stable. Second, no matter what formula is chosen for making the product, there will always be a massive requirement for raw materials.
Their partnership with Minima overcomes both challenges.
Minima has spent the last 17 years perfecting the manufacture of a full suite of single-use plastic alternatives. Their product portfolio includes straws, cups & lids for cold drinks, fast-food bowls & lids for soups, curries and the like, bags, bag liners, Saran wrap- like films for food storage, and cutlery. All of these items are fully certified and are already in production in mass quantities.
That makes Evanesce’s ramp-up to scale fast and simple, with no need for engineering and certification. These things have already been done, making it practically a turn-key operation; all they need to do is raise funds for purchasing the machinery (as mentioned the treasury sits around $16 million), install the equipment, and press “go”.
Straws are just the first step, the “low-hanging fruit,” so to speak.
Considering the size of the packaging market, representing over a third (36%) of all plastic produced, and the number of single-use plastics that could be converted to plant-based compostable items, the opportunities are practically endless.
Evanesce’s Stage 2 growth
Anyone who stops in at their local recycling depot will notice a large bin that is nearly always full. This is polystyrene, more commonly known as Styrofoam. Like single-use plastics, Styrofoam plays a huge role in packaging. The white and multi-colored material is placed in boxes to protect goods especially those being shipped. Meats are set on polystyrene trays to protect the contents before being wrapped in plastic.
It is the latter usage that Evanesce is targeting in its second product line rollout planned for this year. About 800,000 tonnes of meat packaging waste per year is produced in the UK alone. North America uses a similarly large amount. I couldn’t find a figure, but it wouldn’t surprise me to learn it’s in the billions of trays, all going through the polystyrene manufacturing process. All the big food retailers use them — Costco, Walmart, Safeway, etc.
The Styrofoam alternative Evanesce plans on making is 100% compostable but looks and feels identical to polystyrene. Using a manufacturing process known as starch fiber technology, the patent covers a wide range of fibers that are all derived from food waste — from rice and wheat husks to barley and hemp, all may be used in the starch fiber end product. The fact that food waste is so inexpensive, and plentiful, makes it an ideal source of raw materials for Evanesce.
Suppliers include large food processing companies like McCains. Under Evanesce’s patented formula, the starches are mixed with various fibers to produce a material that resembles cookie dough, which is pressed into a mold, placed on a tray and cooked on a conveyor as it passes through a large oven.
Like its straws, Evanesce’s Styrofoam alternative is cost-competitive. Evanesce won’t beat polystyrene on price, but it will be a percentage, not a magnitude, higher, making it easier to interest big meat packing companies like Tyson Foods.
The company’s goal is to to create a product that has the same properties as the meat trays, that allows high-speed packaging machines to seamlessly switch from a polystyrene to a starch-fiber product — one that is fully compostable within 60 days.
Evanesce is targeting the second half of 2022 to have its first starch-fiber machinery up and running. The equipment is being supplied by Buhler Group, one of the largest food processors in the world.
As for clients, Evanesce is getting the attention of some of the largest food distributors in North America, including Novalex, whose Eco-Products insignia is stamped on Starbucks cups, for example. Novalex has a standing order for millions of straws per week and other similar distributors have placed multi-million-unit orders per week as well.
Conclusion
This tremendous $980 billion market opportunity is driven by the change in sweeping government regulation creating a vacuum in the market by banning single-use plastics. Consider: Evanesce’s production lines can each manage a million straws a day. If each production line generates $12 million a year in sales, the company’s goal of 14 lines would generate an annual $160 million just from straws alone.
Evanesce has what we at AOTH love to see in a start-up, and that is cash flow. It’s already landed major clients like Novalex, with cumulative orders exceeding their current production capacity of over 10 million straws per week. Clients will almost certainly increase their orders once the company delivers on time and with quality product. The market for plastic straws is valued at $4 billion a year. If Evanesce could capture even half of the $1.4 billion paper straw market, with their better biopolymer straws at a better price, that’s an annual $700 million.
But plastics straws are only one part of single-use plastics. There’s also the cups, lids, take-out foodware, bags, cling-film, cutlery etc. These markets must be worth billions as well and Evanesce’s biopolymer-based products made from food waste materials are all fully certified compostable, and scaled to mass production, formerly produced in Taiwan. With Evanesces 81%-owned, exclusive manufacturing joint venture transitioning to North America, huge transportation and distribution savings further assists them in being the most cost-competitive alternative in the market.
And we still have to factor in Evanesce’s starch-fiber alternative to Styrofoam. According to a December market research report, the polystyrene market in 2020 was valued at US$9.21 billion. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.1%, reaching $13.1B by 2028. It’s a bit early to be putting a dollar figure on Evanesce’s expected Molded Starch production, but it’s got to be a very nice cash cow, to complement their alternatives to plastic business which already has anchor clients like Novalex.
I heard about the company through Brad Aelicks President of Pyfera Growth Capital Corp, and I participated in an early financing. Pyfera and Aelicks led the financings, the first of which in 2021 raised C$3.9 million, with the second one closing in October at $10.1 million. During that time shareholders exercised about $2.1 million of the warrants that were included in the first financing. In total the company’s financing package amounts to about $16 million, from which Evanesce plans to purchase the first eight straw manufacturing lines. Each line can produce approximately a million straws a day when operating on three shifts per day. Two production plants, one in South Carolina and the other in Las Vegas, will provide central distribution points for both the mass markets along the US Eastern Seaboard and the West Coast.
Alternatives to single-use plastic is an idea whose time has come. Evanesce is clean, green, “ESG-friendly” (environmental, social and governance, the buzzword of the day). It has the right story to tell at the right time in the market. I am eagerly awaiting the IPO, expected this year, and will keep my readers informed of the company’s progress as it gets all its ducks in a row for commercial production of plant-based biopolymer straws, along with Molded Starch products including meal trays, meat trays, containers and cups.
Richard (Rick) Mills
aheadoftheherd.com
subscribe to my free newsletter
Legal Notice / Disclaimer
Ahead of the Herd newsletter, aheadoftheherd.com, hereafter known as AOTH.
Please read the entire Disclaimer carefully before you use this website or read the newsletter. If you do not agree to all the AOTH/Richard Mills Disclaimer, do not access/read this website/newsletter/article, or any of its pages. By reading/using this AOTH/Richard Mills website/newsletter/article, and whether you actually read this Disclaimer, you are deemed to have accepted it.
Any AOTH/Richard Mills document is not, and should not be, construed as an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to purchase or subscribe for any investment.
AOTH/Richard Mills has based this document on information obtained from sources he believes to be reliable, but which has not been independently verified.
AOTH/Richard Mills makes no guarantee, representation or warranty and accepts no responsibility or liability as to its accuracy or completeness.
Expressions of opinion are those of AOTH/Richard Mills only and are subject to change without notice.
AOTH/Richard Mills assumes no warranty, liability or guarantee for the current relevance, correctness or completeness of any information provided within this Report and will not be held liable for the consequence of reliance upon any opinion or statement contained herein or any omission.
Furthermore, AOTH/Richard Mills assumes no liability for any direct or indirect loss or damage for lost profit, which you may incur as a result of the use and existence of the information provided within this AOTH/Richard Mills Report.
You agree that by reading AOTH/Richard Mills articles, you are acting at your OWN RISK. In no event should AOTH/Richard Mills liable for any direct or indirect trading losses caused by any information contained in AOTH/Richard Mills articles. Information in AOTH/Richard Mills articles is not an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any security. AOTH/Richard Mills is not suggesting the transacting of any financial instruments.
Our publications are not a recommendation to buy or sell a security – no information posted on this site is to be considered investment advice or a recommendation to do anything involving finance or money aside from performing your own due diligence and consulting with your personal registered broker/financial advisor.
AOTH/Richard Mills recommends that before investing in any securities, you consult with a professional financial planner or advisor, and that you should conduct a complete and independent investigation before investing in any security after prudent consideration of all pertinent risks. Ahead of the Herd is not a registered broker, dealer, analyst, or advisor. We hold no investment licenses and may not sell, offer to sell, or offer to buy any security.
Legal Notice / Disclaimer
Ahead of the Herd newsletter, aheadoftheherd.com, hereafter known as AOTH.Please read the entire Disclaimer carefully before you use this website or read the newsletter. If you do not agree to all the AOTH/Richard Mills Disclaimer, do not access/read this website/newsletter/article, or any of its pages. By reading/using this AOTH/Richard Mills website/newsletter/article, and whether you actually read this Disclaimer, you are deemed to have accepted it.